API Chaining and Dynamic Parameter Usage
You can combine values from previous API steps, test data, and example variables in your API requests. This makes your tests flexible, realistic, and fully data-driven.
What Is API Chaining?
API Chaining lets one API step use data returned from a step that came before it.
You can reuse response data such as tokens, IDs, or user details in the URL, headers, query parameters, or body of another request.
Examples
Chaining is useful when:
- A token or ID from Step 1 is required in Step 2
- You want to reproduce real-world multi-step workflows
- Your test relies on values generated at runtime
How to Chain API Steps
Add an API Step
Create the first API step, such as a login or credential fetch.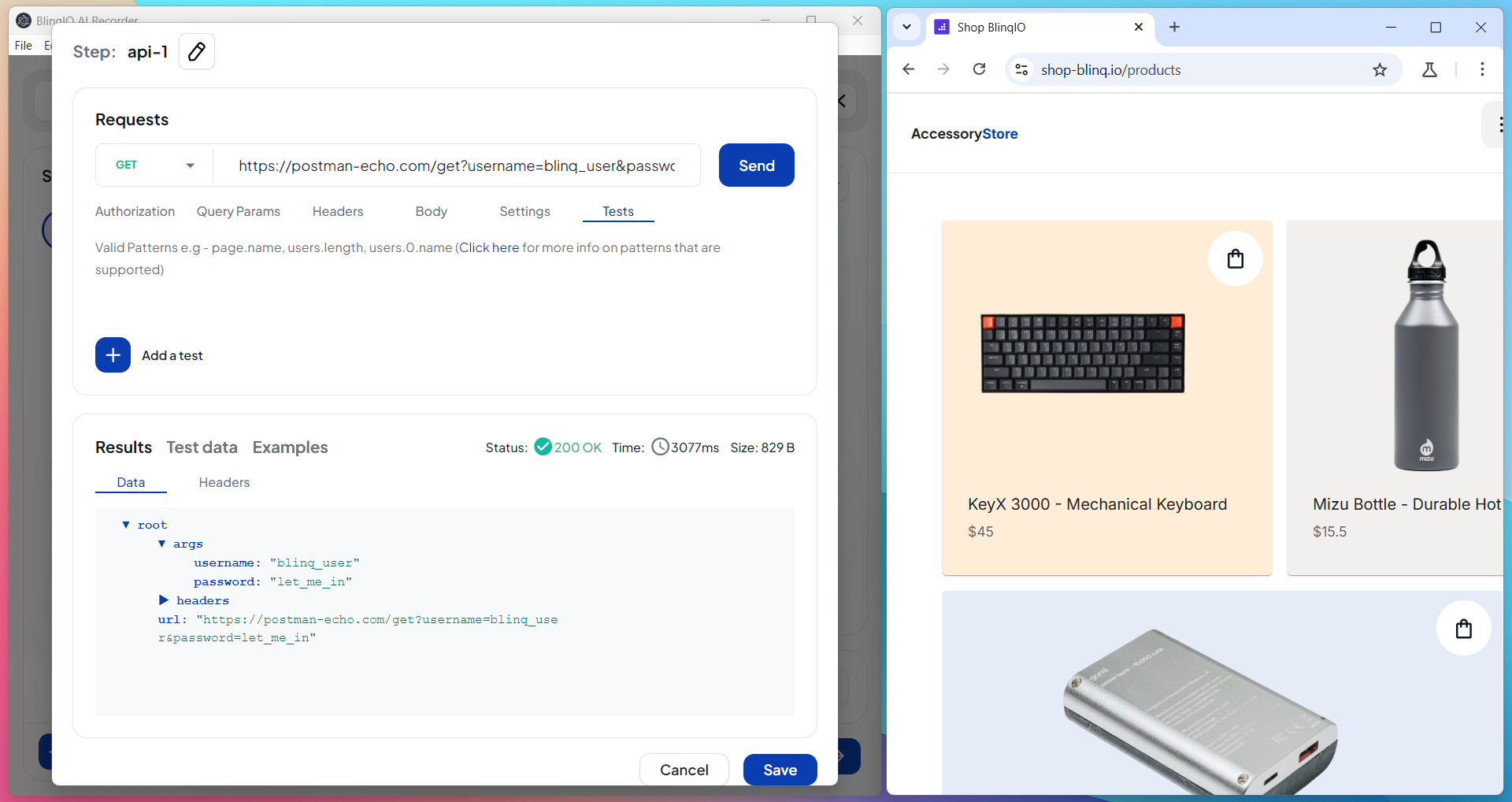
Note
See Add an API Step for details.
Save the Step
Once the step is saved, its response is available as test data for future steps. The response will appear under the step name.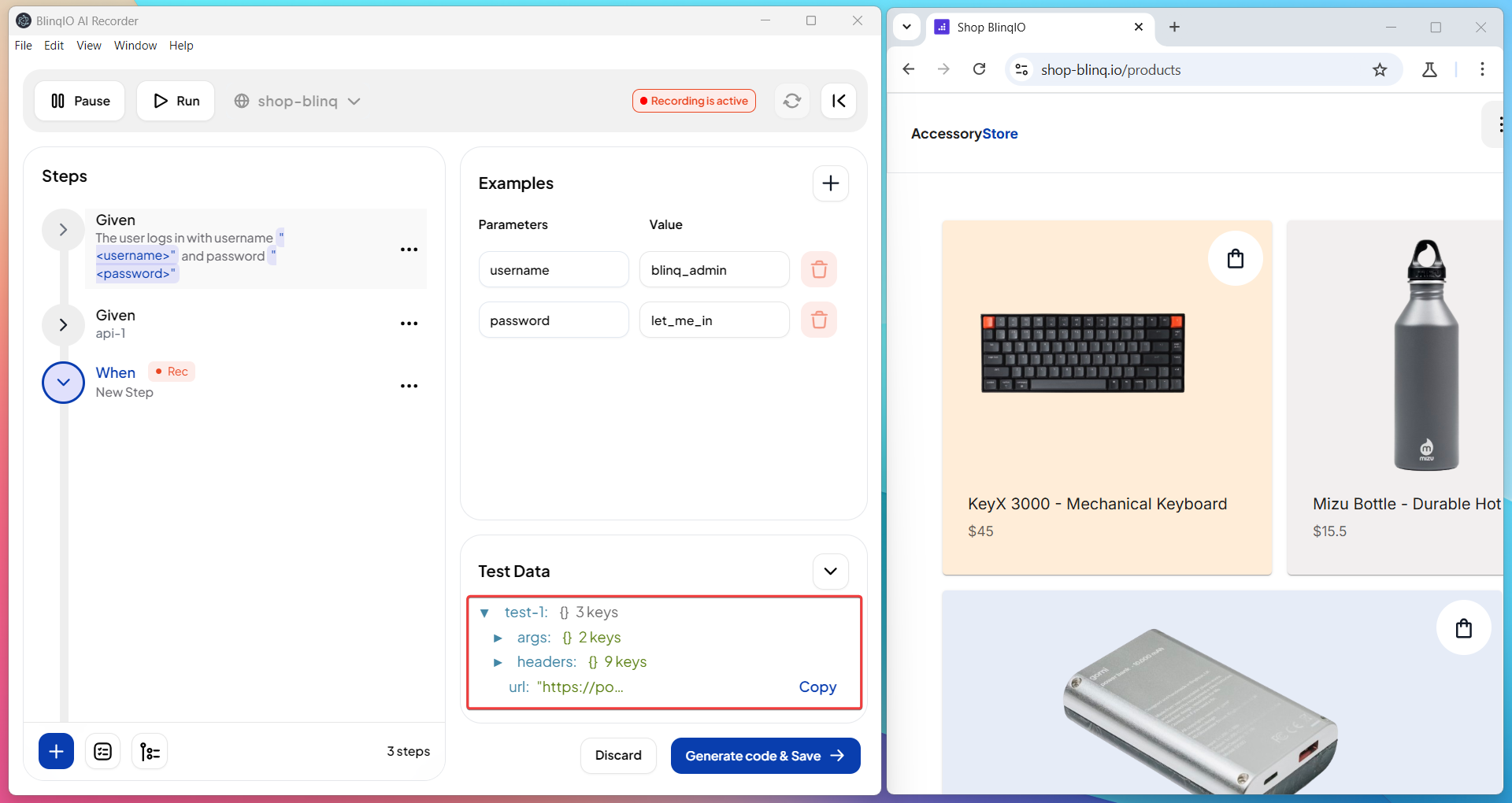
Note
See Save an API Step.
Add the Next API Step
- Open the Test Data section.
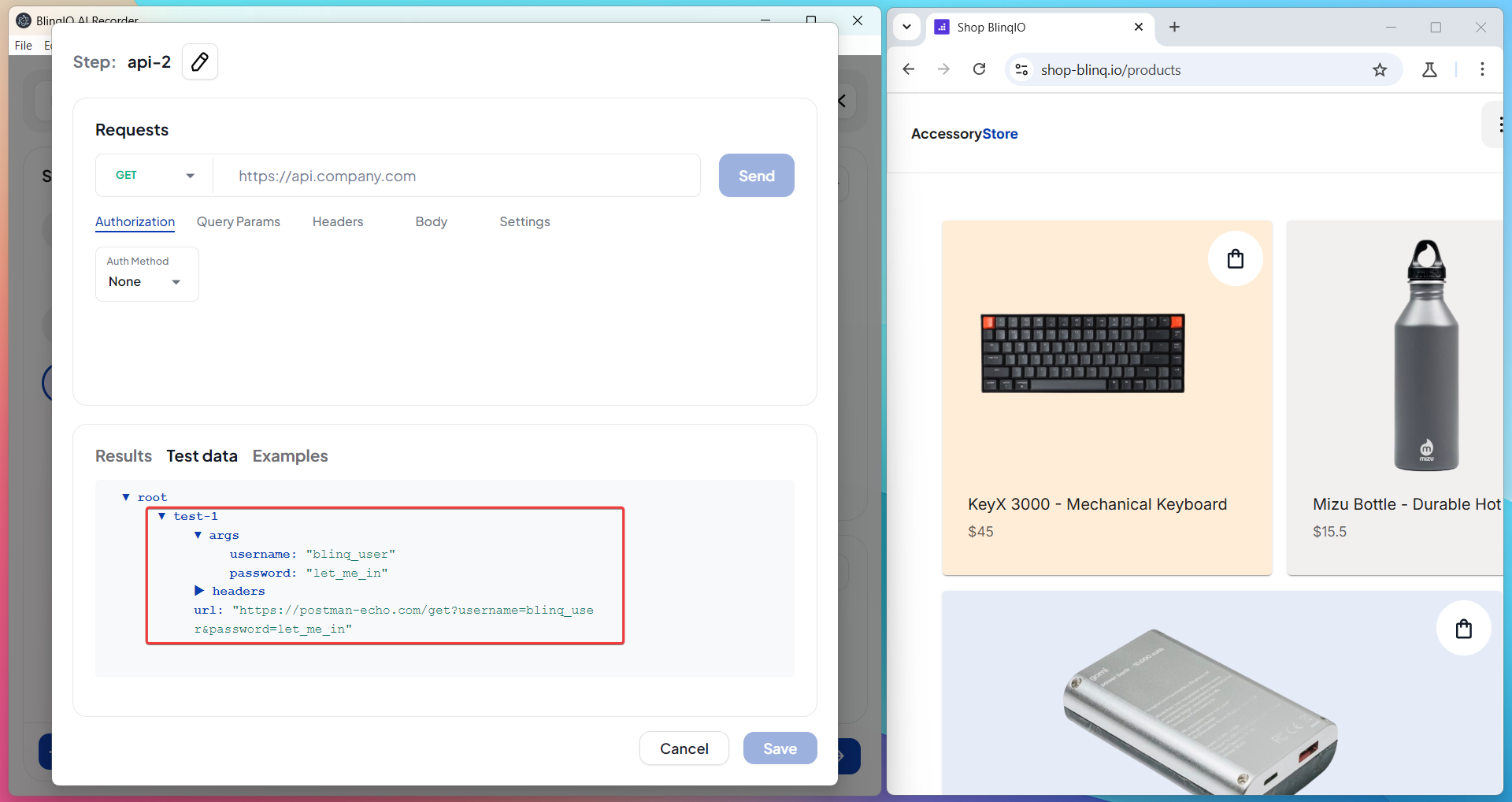
- You will see the response fields from the previous step.
- Click a field to copy its syntax.
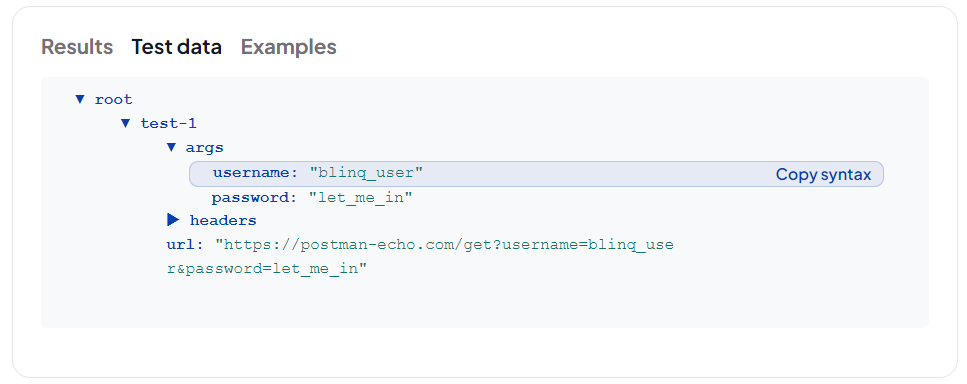
- Open the Test Data section.
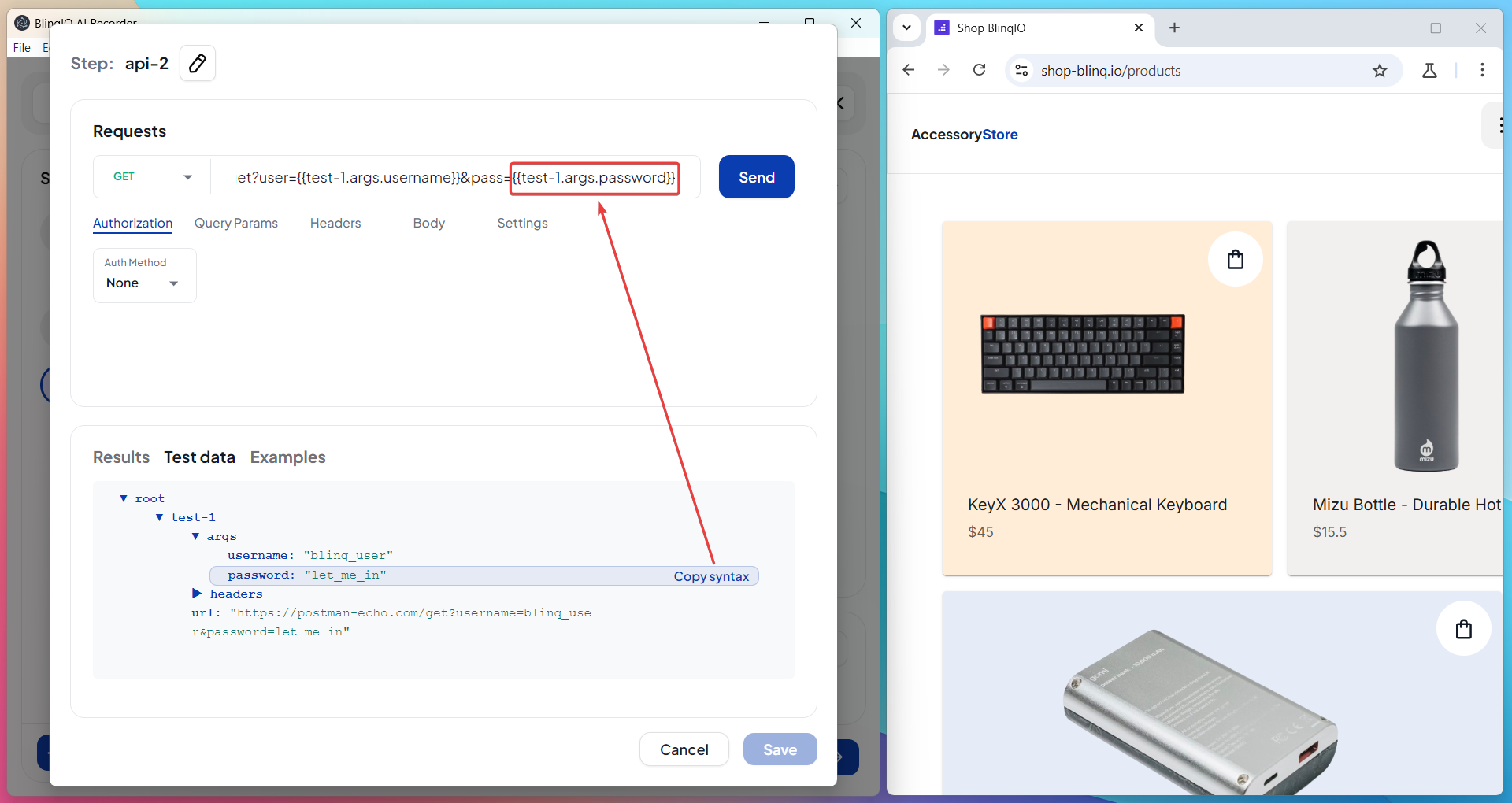
Use the Response in Request Fields
Paste the copied value into any request field that supports dynamic input (URL, headers, query parameters, or body).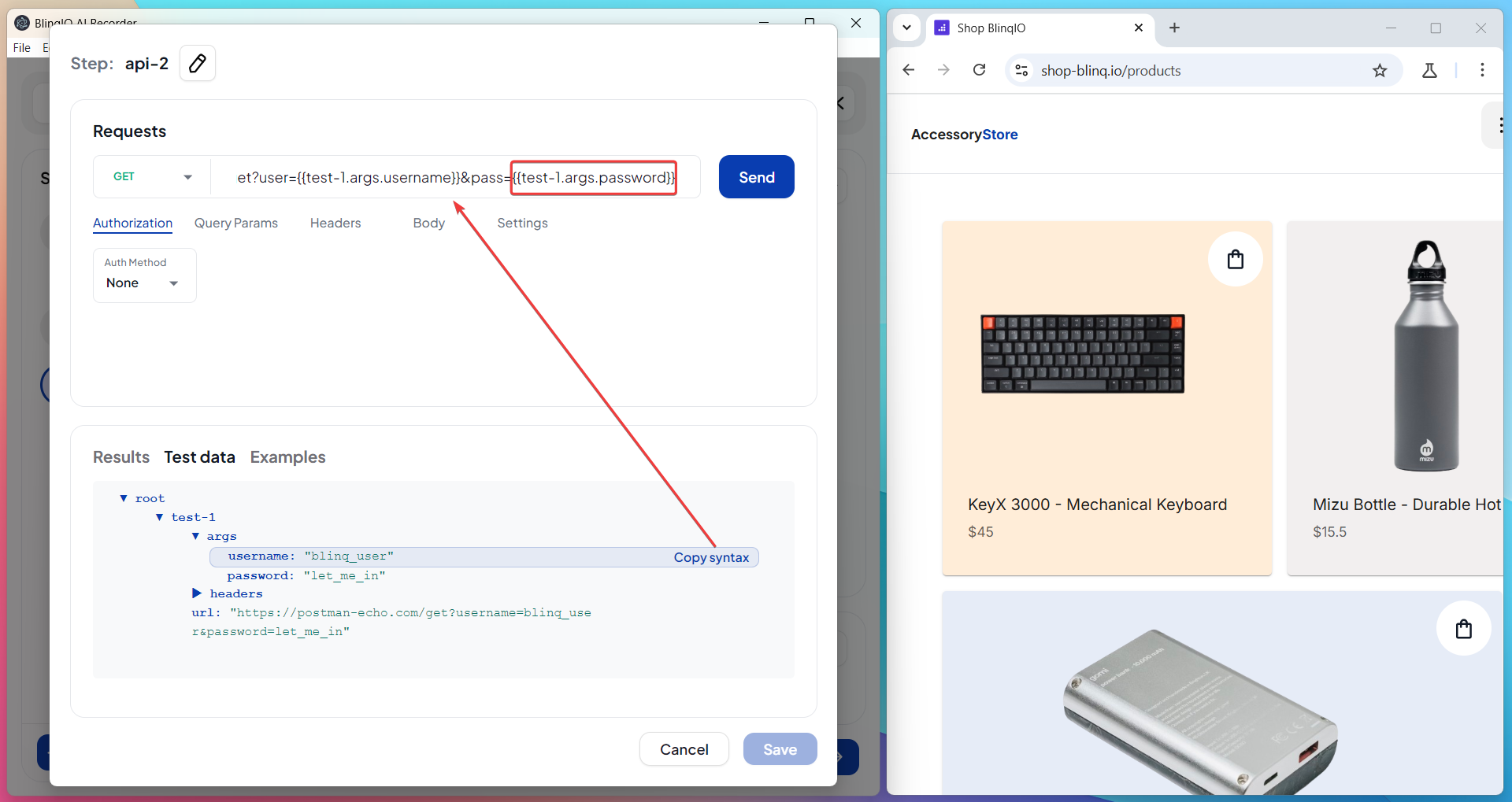
Send the Request and Confirm the Result
Trigger the request and verify that the chained values are applied correctly.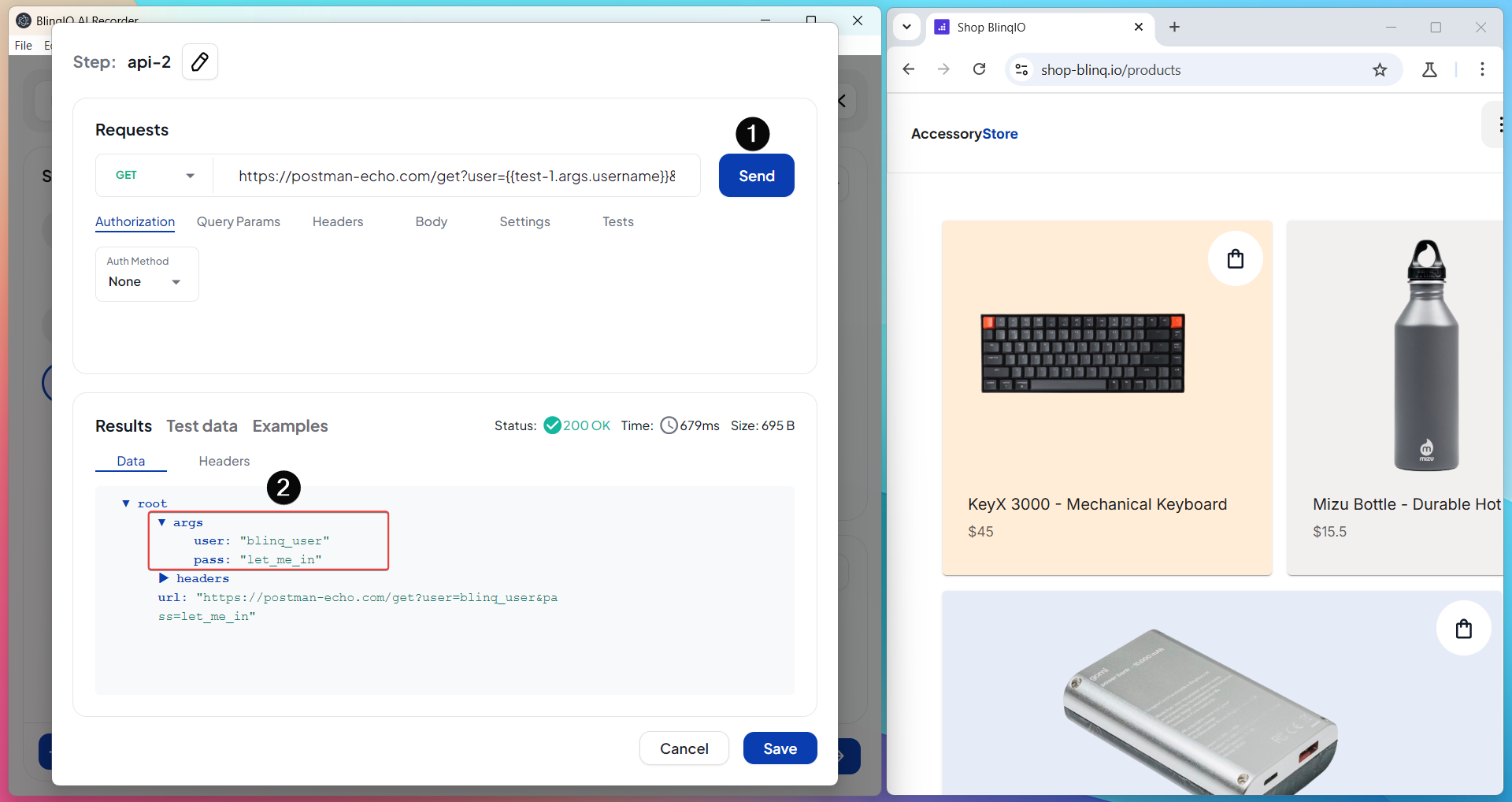
Using Dynamic Parameters in Any Request Field
In addition to chaining responses, you can also use values from Examples or Test Data in your API steps.
Supported Dynamic Values
| Parameter Type | Syntax | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Example Variables | <variableName> | Scenario-level Examples table |
| Test Data Values | {{testDataName}} | Test Data section |
| Chained Response Data | {{step-1.responsePath}} | Response of previous API steps |
You can use dynamic values in:
- URL (as shown above in chaining)
Note
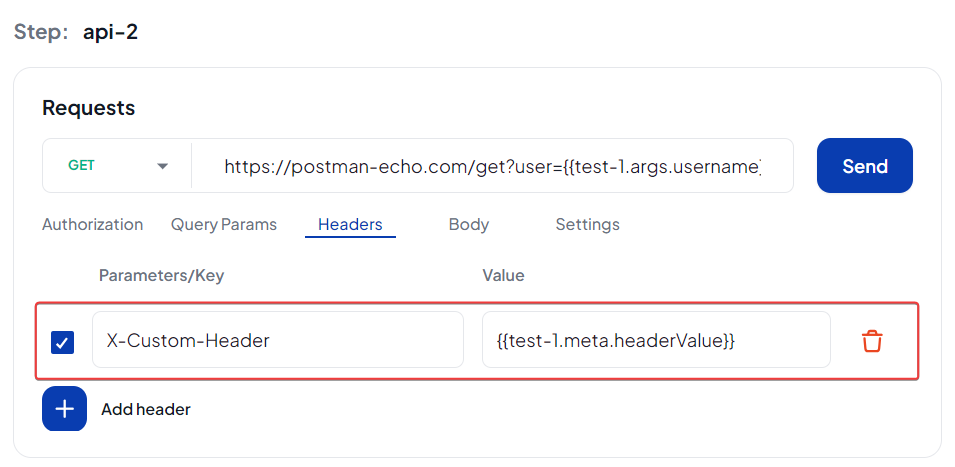
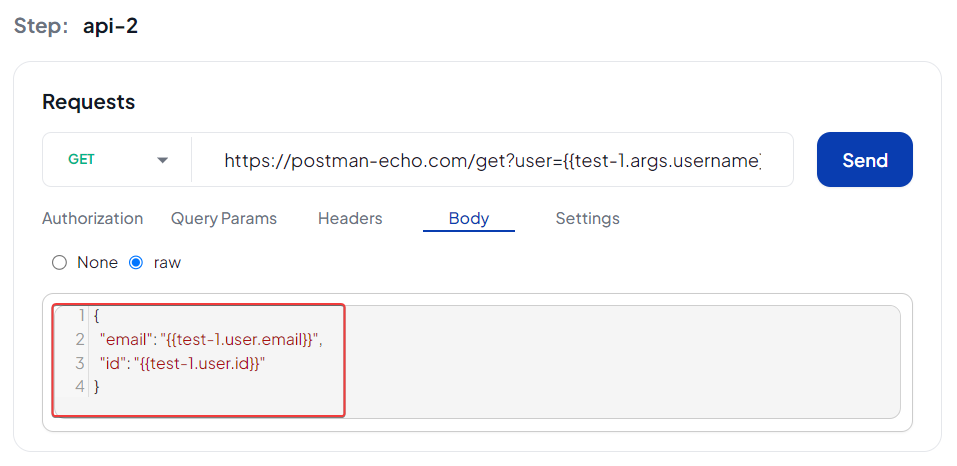
The screenshots below use response data as examples. The same process works for Test Data values ({{testDataName}}) and Example variables (<exampleVariable>).
You can also combine different types of parameters in the same request field.
Query Parameters
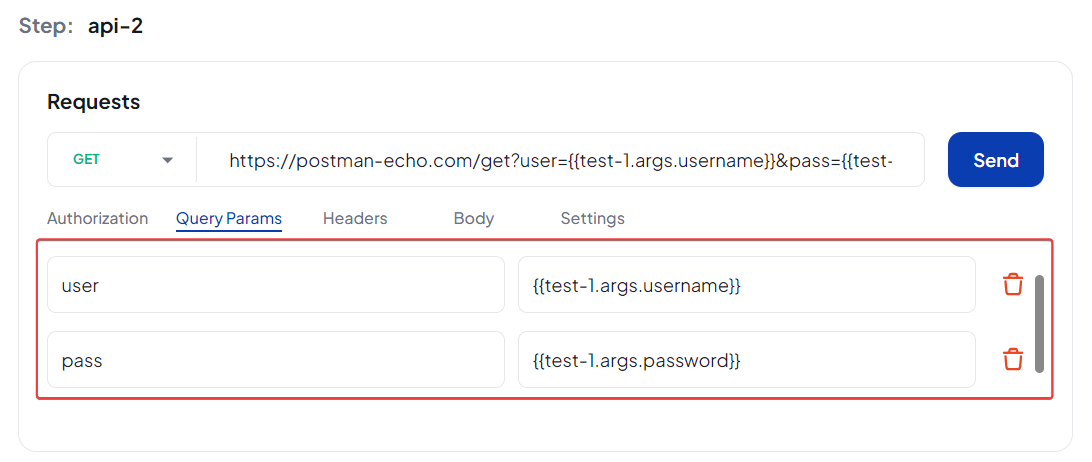
Headers
Request Body
Best Practices
- Save step responses with clear names so they are easier to reference later.
- Only chain important values, such as tokens or IDs, to keep requests simple.
- Use Example variables for reusable scenarios and Test Data for flexible input.
- Always re-run requests after editing to confirm values are resolved correctly.
- Combine different parameter sources thoughtfully to build realistic workflows.
